Still dreaming of buying a home on retirement income?
You can use Social Security income to get an FHA loan. Some lenders can even gross up the non-taxable portions of the benefits you received by 15%. This increase in income boosts your chances of qualifying for a mortgage.
According to the Federal Housing Administration, your Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), Supplemental Security Income (SSI), and retirement benefits count as income as long as they’ll continue for at least 3 years.
Below, we’ll share the steps and requirements on how to get approved for an FHA loan using your retiree income.
Using Social Security Income for FHA Loan Qualification
If you’re a retiree or a senior citizen who receives Social Security benefits, you can apply for FHA home loans using the benefits as a reliable source of income. FHA also recognizes other types of qualifying income sources that can get you approved for a mortgage.
Qualifying Social Security Income Types:
- Social Security retirement benefits
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
- Social Security survivor benefits
The key advantage for Social Security recipients is that FHA loans offer more flexible debt to income ratio requirements compared to conventional loans, allowing up to 57% total debt to income ratio with compensating factors.
FHA Gross Up Social Security Income Guidelines
Understanding the 15% FHA Gross Up Rule
Under FHA guidelines, mortgage lenders can increase non-taxable income like Social Security by 15% when calculating your qualifying income. This increase in qualifying income can help you get approved for a larger mortgage amount.
Gross Up Calculation Example:
- Monthly Social Security Income: $2,000
- FHA 15% Gross Up: $300 ($2,000 × 0.15)
- Total Qualifying Income: $2,300
This additional $300 monthly can increase your home loan purchasing power by approximately $15,000-20,000, depending on current mortgage rates and your debt to income ratio.
How FHA Gross Up Compares to Other Loan Programs
| Loan Program | Gross Up Percentage | $2,000 Monthly Income Becomes |
|---|---|---|
| FHA Loan | 15% | $2,300 |
| Conventional Loans | 25% | $2,500 |
| VA Loans | 25% | $2,500 |
| USDA Loans | 25% | $2,500 |
While conventional loans offer higher gross up percentages, FHA loans provide other advantages like lower down payment requirements and more flexible credit score guidelines that often make them the better choice for Social Security recipients.
Documentation Requirements for Social Security Income
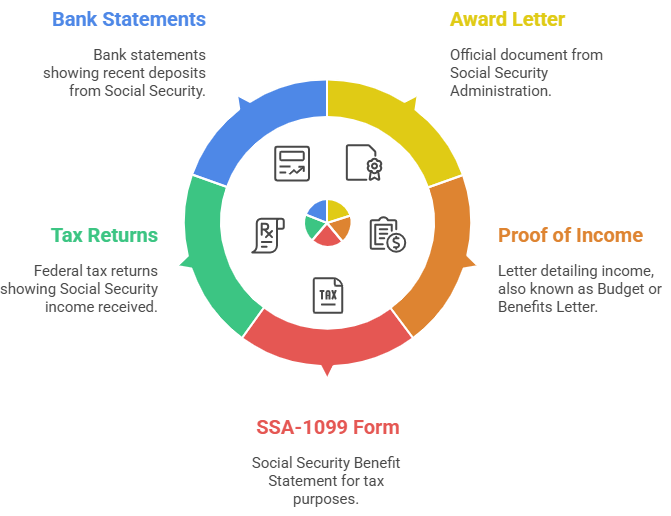
Mortgage lenders must verify Social Security income through acceptable documentation. The Federal Housing Administration requires one of the following documents:
Primary Documentation Options:
- Social Security Administration Award Letter (most preferred)
- SSA Proof of Income Letter (Budget Letter or Benefits Letter)
- Form SSA-1099 (Social Security Benefit Statement)
- Federal tax returns showing Social Security income
- Bank statements evidencing recent SSA deposits
The Three-Year Continuation Requirement
Critical FHA Guideline: Social Security income must be likely to continue for at least three years from the mortgage application date. This requirement applies to all income sources used for FHA loan qualification.
Automatic Qualification:
- Retirement Social Security benefits
- Permanent disability benefits (SSDI)
- Long-term SSI benefits
Additional Documentation Needed:
- Benefits with stated expiration dates
- Benefits received on behalf of others
- Temporary disability benefits
If your Social Security benefits expire within three years, they cannot be used as effective income for FHA loan qualification, though they may serve as compensating factors in the underwriting process.
FHA Loan vs Conventional Loans for Social Security Recipients
If you’re unsure whether to opt for the government-backed option or go the conventional route, you need to keep a few things in mind. Here’s a rundown of the different benefits of FHA and conventional loans to help you determine which type of loan is best for you.
FHA Loan Advantages for Social Security Income
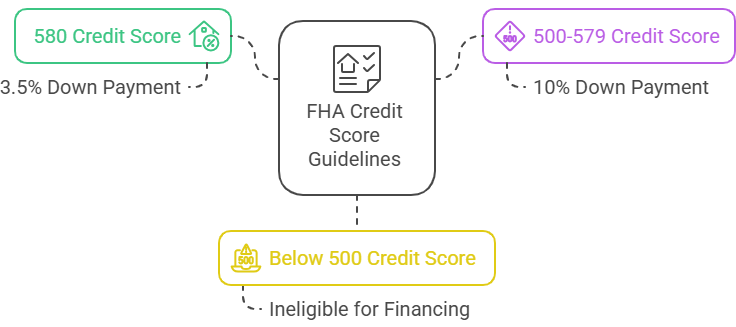
Lower Down Payment: FHA loans require only 3.5% down payment versus 5-20% for conventional loans, making homeownership more accessible for those on fixed income.
Flexible Credit Score Requirements: FHA accepts credit scores as low as 580 (or 500 with 10% down), while conventional loans typically require 620 minimum.
Higher Debt to Income Ratio: FHA allows up to 57% total debt to income ratio with strong compensating factors, versus 45-50% for most conventional loans.
Gift Funds Allowed: 100% of the down payment can come from eligible gift sources including family members, employers, or charitable organizations.
When Conventional Loans May Be Better
Higher Gross Up Percentage: Conventional loans allow 25% gross up on non-taxable Social Security income versus 15% for FHA loans.
No Mortgage Insurance with 20% Down: Eliminates monthly mortgage insurance premiums if you can afford a larger down payment.
Higher Loan Limits: Conventional loan limits may exceed FHA limits in some high-cost areas.
Debt to Income Ratio Guidelines for FHA Social Security Income
Your DTI or debt to income ratio shows how much of your FHA Social Security income goes toward loan and debt payments.
FHA DTI Requirements
FHA mortgage lenders evaluate both front-end and back-end debt to income ratios when qualifying Social Security recipients:
Front-End DTI (Housing Ratio):
- Maximum 31% of gross monthly income
- Includes mortgage payment, property taxes, homeowners insurance, and HOA fees
Back-End DTI (Total Debt Ratio):
- Maximum 43% of gross monthly income (can go up to 57% with compensating factors)
- Includes housing payment plus all monthly debt obligations
Calculating Your Qualifying Income
Example Scenario:
- Social Security Income: $1,800/month
- 15% FHA Gross Up: $270
- Total Qualifying Income: $2,070
- Maximum Housing Payment (31%): $642
- Maximum Total Debt (43%): $890
This calculation shows how the gross up provision can significantly impact your home loan qualification amounts.
Investment Income and Additional Income Sources
Getting a mortgage using your Social Security income is possible, but challenging. To satisfy your lender’s income requirements and boost your mortgage application approval, think about combining your Social Security with other income sources.
Combining Social Security with Other Income
Many Social Security recipients have additional income sources that can strengthen their FHA loan application:
Pension Income: Can be grossed up if non-taxable, subject to three-year continuation requirement Investment Income: Dividends and interest from stocks, bonds, or savings accounts Rental Income: From investment properties (subject to specific FHA guidelines) Part-Time Employment: Requires two-year history and likelihood to continue
Traditional IRA and Roth IRA Withdrawals
Retirement account withdrawals can supplement Social Security income for FHA loan qualification:
Traditional IRA: Withdrawals count as income, may be partially taxable Roth IRA: Tax-free withdrawals may qualify for gross up treatment Documentation Required: Account statements showing sufficient balance for three-year continuation
Credit Score Requirements and Compensating Factors
The higher the credit score, the better your chances of qualifying for a home loan. But in cases where a Social Security recipient has a low score, FHA may consider other compensating factors.
FHA Credit Score Guidelines
Minimum Credit Score Requirements:
Compensating Factors for Social Security Recipients
Senior citizens and disabled borrowers often have strong compensating factors that can offset higher debt to income ratios:
Asset Reserves: Substantial savings or retirement accounts Stable Income History: Long-term receipt of Social Security benefits Minimal Housing Payment History: Low probability of payment shock Conservative Mortgage Payment: Choosing affordable monthly payments relative to income
FHA Loan Programs and Options
FHA offers loan programs that fit the unique financial situations of retirees and older adults relying on Social Security benefits. Take a look at some options below:
Standard FHA Purchase Loans
Most Social Security recipients qualify for traditional FHA purchase loans with:
- 30-year fixed rate mortgages
- 15-year fixed rate options
- Adjustable rate mortgages (ARM)
FHA Streamline Refinance
Existing FHA borrowers on Social Security can benefit from streamlined refinancing:
- Reduced documentation requirements
- No income verification needed
- No credit check required
- No appraisal needed in most cases
Reverse Mortgages for Senior Citizens
Homeowners aged 62 and older may consider FHA-insured reverse mortgages (HECM):
- Convert home equity into tax-free income
- No monthly mortgage payments required
- Remain in home for life
- Social Security benefits not affected
Common Mistakes and Tips for Success
If you’re looking to secure an FHA loan as a retiree or a senior person, you need to prepare your documents and assess your credit and finances early in the process.
Here are some tips to avoid loan application mishaps and successfully get a mortgage later in life.
Documentation Errors to Avoid
Incomplete Award Letters: Ensure your SSA award letter is current and shows continuation information Missing Bank Statements: Provide complete statements showing consistent Social Security deposits Outdated Tax Returns: Use most recent tax returns if you file them
Maximizing Your Qualification
Timing Your Application: Apply when your Social Security income is stable and documented Pay Down Debt: Reduce monthly obligations to improve debt to income ratio Save for Larger Down Payment: Consider 10% down to potentially qualify with lower credit scores Consider Co-Borrowers: Eligible family members can strengthen the application
Loan Officer Guidance and Professional Help
Finding an experienced loan officer can help you process your application and get you the best deal.
Working with Experienced Mortgage Lenders
Choose mortgage lenders experienced with Social Security income verification:
- FHA-approved lenders familiar with gross up guidelines
- Local knowledge of area home prices and loan limits
- Experience with senior and disabled borrower needs
Questions to Ask Your Loan Officer
Income Calculation: “How will you calculate my grossed-up Social Security income?” DTI Flexibility: “What compensating factors can help if my debt to income ratio is borderline?” Loan Options: “Should I consider FHA or conventional based on my specific situation?” Timeline: “How long will the mortgage process take with Social Security income documentation?”
First Time Buyers and Social Security Income
Purchasing your first home can be an overwhelming experience. Thankfully, several programs and FHA’s flexible guidelines can help make homeownership more accessible for seniors and retirees using Social Security income.
Special Considerations for First-Time Homebuyers
First time buyers using Social Security income have unique advantages:
- Homebuyer education courses may strengthen application
- Down payment assistance programs often available
- FHA’s flexible guidelines accommodate non-traditional income
- Various state and local programs for seniors and disabled buyers
Understanding Homeownership Costs
Beyond the Mortgage Payment:
- Property taxes and homeowners insurance
- Maintenance and repairs
- Utilities and ongoing expenses
- HOA fees if applicable
Plan conservatively to ensure comfortable monthly payments that fit your fixed income budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use Social Security income if it’s my only income source?
Yes, Social Security income alone can qualify you for an FHA loan if it meets the lender’s income requirements and debt to income ratio guidelines. The 15% gross up provision often helps Social Security-only applicants qualify.
What if my Social Security income varies month to month?
Lenders typically use the consistent base amount from your award letter. If you receive varying amounts due to cost-of-living adjustments, provide documentation showing the adjustment history.
Do I need to file tax returns to use the gross up?
No, FHA allows the 15% gross up on Social Security income even if you don’t file tax returns. However, if you do file returns, they may be required for income verification.
Can I buy a second home or investment property with Social Security income?
FHA loans are only for owner-occupied primary residences. Investment income property purchases would require conventional loans or other financing options.
How does divorce affect Social Security income for FHA loans?
Divorced spouse Social Security benefits are treated the same as any other Social Security income for FHA qualification purposes, subject to the same documentation and continuation requirements.



